- info@paca-environnement.com
- 1 rue du Gabian – Le Thalès 98000 Monaco
Other products

Do you have a question?

Other products
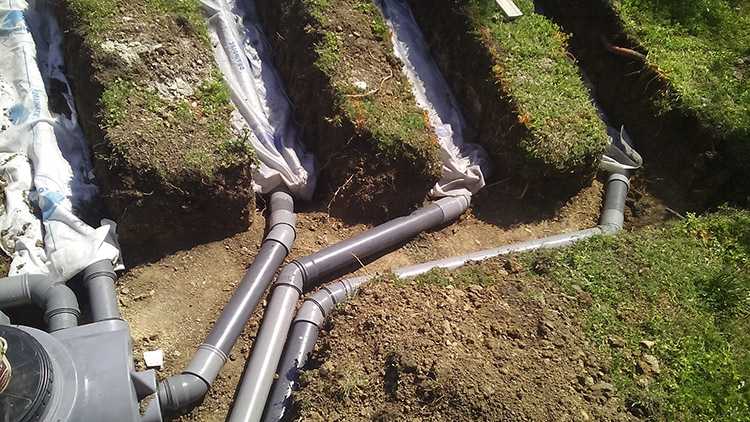
As part of the installation of non-collective sanitation, a connection to the sewer, rainwater management or a VRD project, numerous peripheral products will be implemented.
In non-collective sanitation (ANC)
The materials needed to create an ANC depend on the type of sewerage system that will be selected, the size of your property, soil characteristics, local regulations and other specific factors.
However, here is a general list of components and hardware commonly used for creating an ANC:
1. Treatment unit (all-water pit, micro-station or compact sector)
The processing unit is one of the key components of an ANC. It is one or more underground tanks intended for the separation and initial decomposition of solid materials in wastewater. Processing units are usually made of concrete, plastic or fiberglass. The choice of material depends on local preferences, terrain type and regulations.
2. Pipelines and manholes:
You will need pipes to carry wastewater from your home to the treatment unit, as well as from the treatment unit to other components in the system. Collection and/or inspection manholes will be necessary for control and maintenance of the system.
3. Spreading or infiltration system:
If your ANC system includes post-treatment in the soil, you will need a spreading bed or infiltration bed. These areas allow treated or pre-treated water to slowly seep into the ground for further purification. A certain number of modern and ecological solutions exist to shorten the size of drains or to make their construction less expensive. (Ex: Drainotec©, Graf© tunnels, etc…).
4. Lift pump (if necessary):
In situations where the soil does not have adequate infiltration capacity or where your home is located downhill from a slope, you may need a lift pump to convey wastewater to the bed. infiltration or other devices.
5. Ventilation pipes:
Vent pipes allow air to circulate through the ANC system to prevent backflows and facilitate the wastewater treatment process. Modern photovoltaic ventilation systems make it possible to no longer distort the facades of houses, since they can be installed on the ground.
6. Control equipment:
ANC systems may include control devices to monitor and regulate system operation, such as alarms, level floats and electronic control systems.
Connected to the sewer
The materials needed for a sewer connection will depend on the specific situation of your property and the requirements of your local authority.
However, here is a general list of equipment commonly used for connection to a public sewer system:
1. Sewer pipes:
PVC pipes: These pipes are used to transport wastewater from your property to the public sewer system. Pipe material and diameter will be determined by local building codes and sewer specifications.
2. Fittings and joints:
- Elbows, tees, reducers, and other fittings: These are necessary to connect sewer pipes properly and to ensure watertight joints.
- Gaskets: These are used to prevent leakage of waste water at joints between pipes and fittings.
3. Trench:
A trench will be dug from your property to the public sewer line to accommodate the sewer pipes. The size of the trench will depend on the diameter of the pipes and the depth to which they are to be installed.
4. Connection fitting and inspection points:
A service fitting is used to connect the sewer pipes on your property to the public sewer system. This fitting is usually installed in the main sewer line and is connected to the pipes on your property. Collection and/or inspection manholes will be necessary for control and maintenance of the system.
5. Backfill:
Backfill material will be required to fill the trench after the sewer pipes are installed, ensuring the pipes are properly supported and protected.
6. Inspection:
Inspection camera: An inspection camera can be used to check the quality of the installation and the correct connection of the pipes before closing the trench.
It is important to note that connecting to a public sewer system is generally a task that should be carried out by qualified professionals, in accordance with local regulations. Do not hesitate to consult our sales engineers regarding specific information on connection requirements in your municipality.
Rainwater management
The equipment needed for rainwater management depends on the specific needs of the project, the size of the area to be managed, and the water management objectives.
Here is a list of equipment and components commonly used in stormwater management:
1. Rainwater collectors:
- Gutters: They collect rainwater that runs off the roofs of buildings.
- Drains: These devices collect rainwater from impervious surfaces, such as roads, parking lots, sidewalks, and parking areas.
- Gutters: Gutters collect rainwater along roadsides and paved areas.
2. Rainwater storage systems:
- Cisterns or reservoirs: They store rainwater for later use, such as irrigation or reuse in toilets.
- Storage basins: Temporary storage basins help slow the flow of rainwater, reduce flow peaks and minimize flooding.
3. Filtration and treatment systems:
- Water Filters: Water filters are used to remove contaminants, particles and pollutants from stormwater before discharge into the environment or reuse.
- Unclogging systems: They help maintain the performance of the filters by eliminating accumulated sediments.
4. Flow management devices:
- Oil separators: They separate oils and greases from rainwater.
- Infiltration structures: They allow rainwater to infiltrate into the ground, thus helping to recharge groundwater tables.
5. Pipes, pipes and manholes:
- PVC or concrete pipes: They transport rainwater from collectors to storage systems, retention basins or treatment devices.
- Drainage pipes: These carry water to suitable dispersion or discharge areas.
- Collection and/or inspection manholes: They will be necessary for the control and maintenance of the system.
6. Dispersal devices:
- Dispersion ditches: They allow rainwater to be distributed over a larger surface area, thus promoting its infiltration or controlled flow.
- Retention basins: They temporarily retain rainwater before allowing it to flow slowly into the drainage system.
7. Monitoring and control equipment:
- Water level sensors: They allow you to monitor water levels in storage basins or pipes.
- Automated control systems: They regulate stormwater management devices based on weather conditions and system status.
Selection of equipment will depend on the specific requirements of the rainmwater management project, local regulations, and water management objectives, such as reducing flooding, protecting water quality, or reusing water.
By calling on PACA Environnement you will have the certainty of working with hydraulic engineering professionals to design and implement an appropriate rainwater management system.
Other products
Our range

DRAINOTEC
Système de drainage innovant fabriqué en France avec agrégats synthétique 100 % recyclé et écologique


EPURACTIF
Ventilation secondaire solaire garantie sans odeurs et sans bruit avec cartouche charbon


TUNNEL GRAF
Système de drainage/infiltration permettant d’accueillir une charge roulante (parking par exemple)

BAC A GRAISSE
Système permettant d’accueillir les eaux grises en amont d’un système d’assainissement


REPORT GSM
Système permettant d’être averti sur votre smartphone lorsque votre station de relevage est en défaut


CHASSE A AUGET
Système permettant d’envoyer des bâchées de 60 à 80 litres vers un drainage
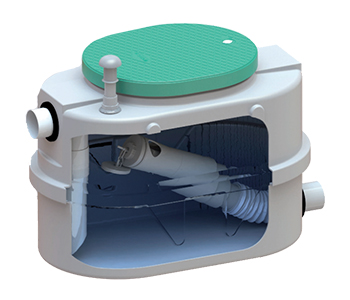

CHASSE A AUGET
Système permettant d’envoyer des bâchées de 50 à 800 litres vers un drainage


CHASSE A AUGET
Système permettant d’envoyer des bâchées de 50 à 800 litres vers un drainage


CHASSE A AUGET
Système permettant d’envoyer des bâchées de 50 à 800 litres vers un drainage


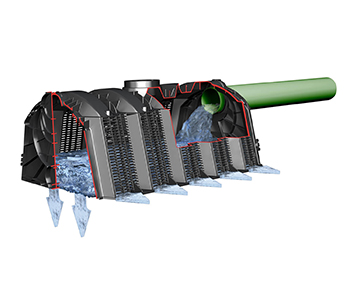
DEGRILLEUR
Ce système permet de bloquer et filtrer les matières en amont d’un système de gestion ou de traitement d’eau


KIT MISE EN PRESSION
Ce kit permet la mise en pression des eaux traitées afin de les épandre harmonieusement


SONDE DEBIT
Cette sonde électronique permet de gérer les variations de débit et ou prévenir d’un éventuel incident


BUSE D’INFILTRATION
Ce système est une alternative à l’épandage habituel, il est utilisé lorsqu’un terrain n’est pas assez grand. La buse infiltre donc de manière verticale (couche profonde de la terre) et non pas de manière horizontale.